One of the many nice features of Xilinx Zynq is ability to run it in Asymmetric MultiProcessing or AMP configuration. Xilinx released version v2013.10 of a UG980(Petalinux Board Bringup) and UG978(Zynq Linux-FreeRTOS AMP) guides for Xilinx ZC702 board. Today I will follow those guides to build Linux-FreeRTOS solution for ZedBoard.
I already have Vivado and Xilinx SDK packages installed along with required, but initially missing packages on my Ubuntu 13.10 64 bit Virtual Machine.
- First of all we will need so called Zynq 'Hardware Platform' which will satisfy both Linux and FreeRTOS minimum requirements.
Linux requires one UART and at least one storage peripheral, for example SD Card. And FreeRTOS also requires one UART and also a Timer.
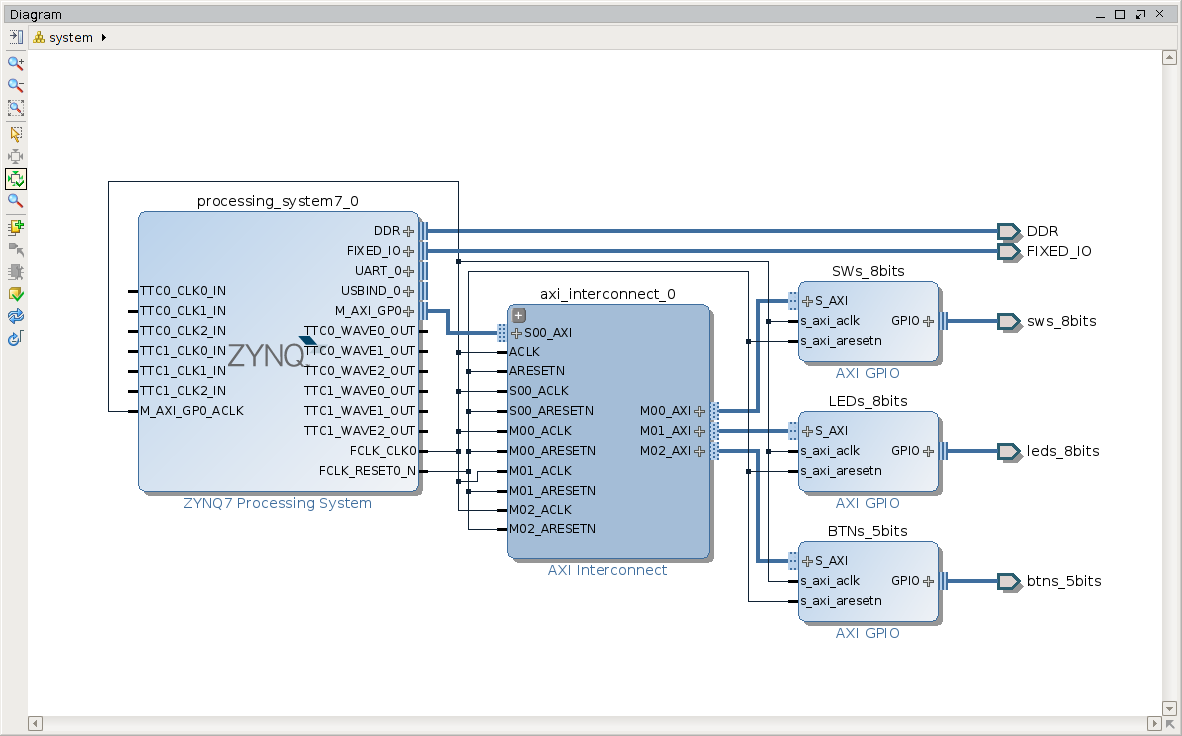
So, I will modify ZedBoard CTT hardware design I created using ZedBoard_CTT_v2013_2_130807 tutorial. That 'Hardware Platform', in addition to base system, consist of 8 switches, 8 led's and 5 push buttons and I will activate 1 more UART and 1 more timer for FreeRTOS.Open Vivado ZedBoard CTT project or create it from scratch using ZedBoard CTT tutorial. I called my project 'ZedBoard-AMP' and made next 2 modifications to CTT design:
- Zynq7 Processing System: MIO Configuration: I/O Peripherals: Enable UART0 and set its IO as 'EMIO'.
- Zynq7 Processing System: MIO Configuration: Application Processor Unit: Enable Timer1 and set its IO as 'EMIO'.
- Run Synthesis, Implementation, generate new BitStream and Export new 'Hardware' to SDK. I prefer not to lauch SDK right away for a good reason - you have to source Xilinx SDK settings and/or PetaLinux settings before running XSDK. After export finished we can close Vivado.
- Lets set required settings and run Xilinx SDK (XSDK). Set 'Eclipse' workspace to our ~/Projects/ directory.
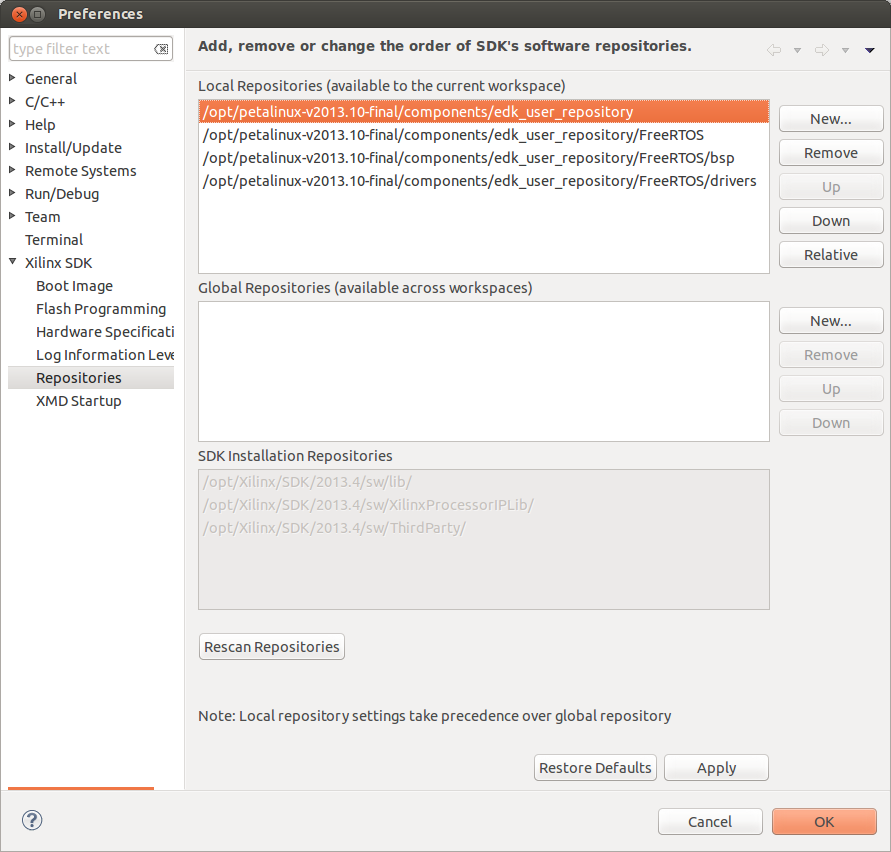
- We need to add PetaLinux and FreeRTOS repositories to XSDK. In XSDK -> Xilinx Tools -> 'Xilinx SDK' -> 'Repositories' -> add 'Local Repositories' from your PetaLinux 13.10 components folder. In my case PetaLinux installed into '/opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/'. So added repo's are:
- /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/components/edk_user_repository
- /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/components/edk_user_repository/FreeRTOS
- /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/components/edk_user_repository/FreeRTOS/bsp
- /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/components/edk_user_repository/FreeRTOS/drivers
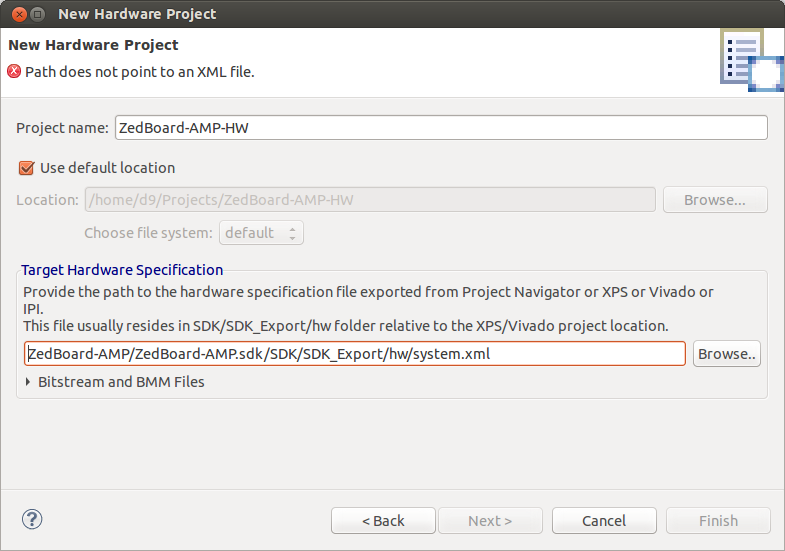
- Create 'Hardware Platform Specification' project using 'Hardware Platfrom' exported from our ZedBoard-AMP Vivado project. I named it 'ZedBoard-AMP-HW'.
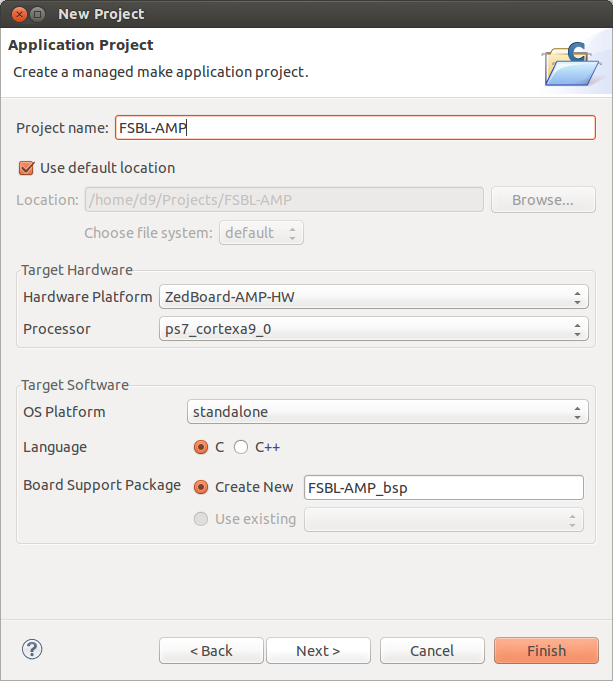
- Create FSBL for AMP configuration using File -> New Project -> Application Project. I named it FSBL-AMP and selected 'ZedBoard-AMP-HW' as Hardware Platform, 'ps7_cortex9_0' as a Processor, 'standalone 'OS Platfrom ', after clicking 'Next' select 'Zynq FSBL' template and finish project creation. Compile both 'FSBL-AMP_bsp' and 'FSBL-AMP' projects if it didnt autobuilt.
- Now we will need to build a few PetaLinux projects, but before we can do this, we have to quit XSDK and source some PetaLinux settings. So, close XSDK, apply settings in next order and launch XSDK again:
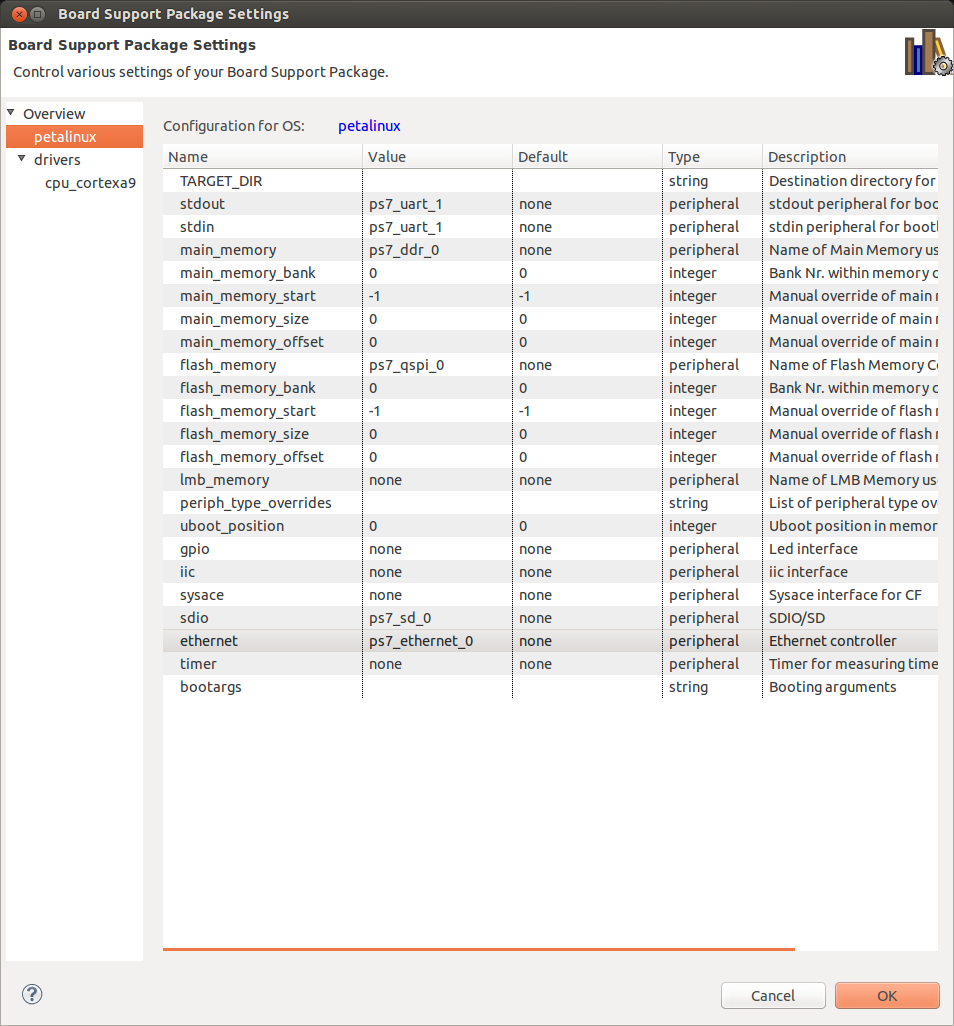
- Create PetaLinux BSP project. In SDK select File -> New -> Project -> 'Board Support Package'. Name it 'petalinux_bsp_amp'. Select 'ZedBoard-AMP-HW' as Hardware Platform, CPU 'ps7_cortexa9_0'. Board Support Package OS 'petalinux'. Then Finish.
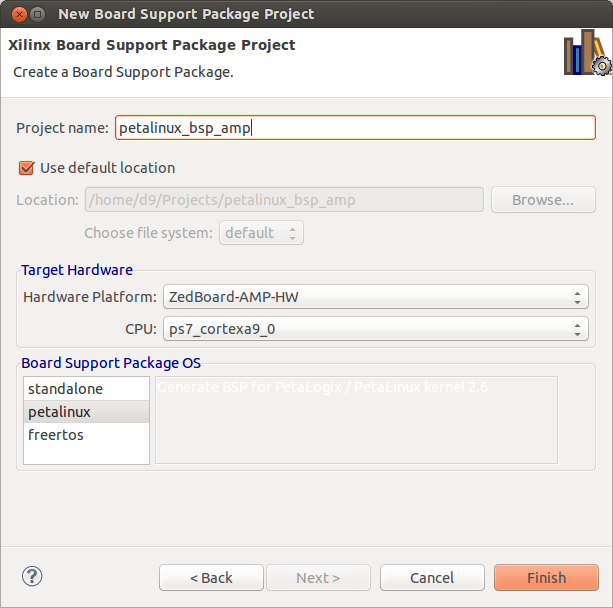
XSDK should automatically open 'Board Support Package Settings' page. Go to 'Overview' -> 'petalinux' menu of that page and set:
- 'ps7_uart_1' for stdout and stdin.
- 'ps7_ddr_0' for main memory.
- 'ps7_qspi' for flash memory.
- 'ps7_sd_0' for sdio.
- 'ps7_ethernet' for ethernet.
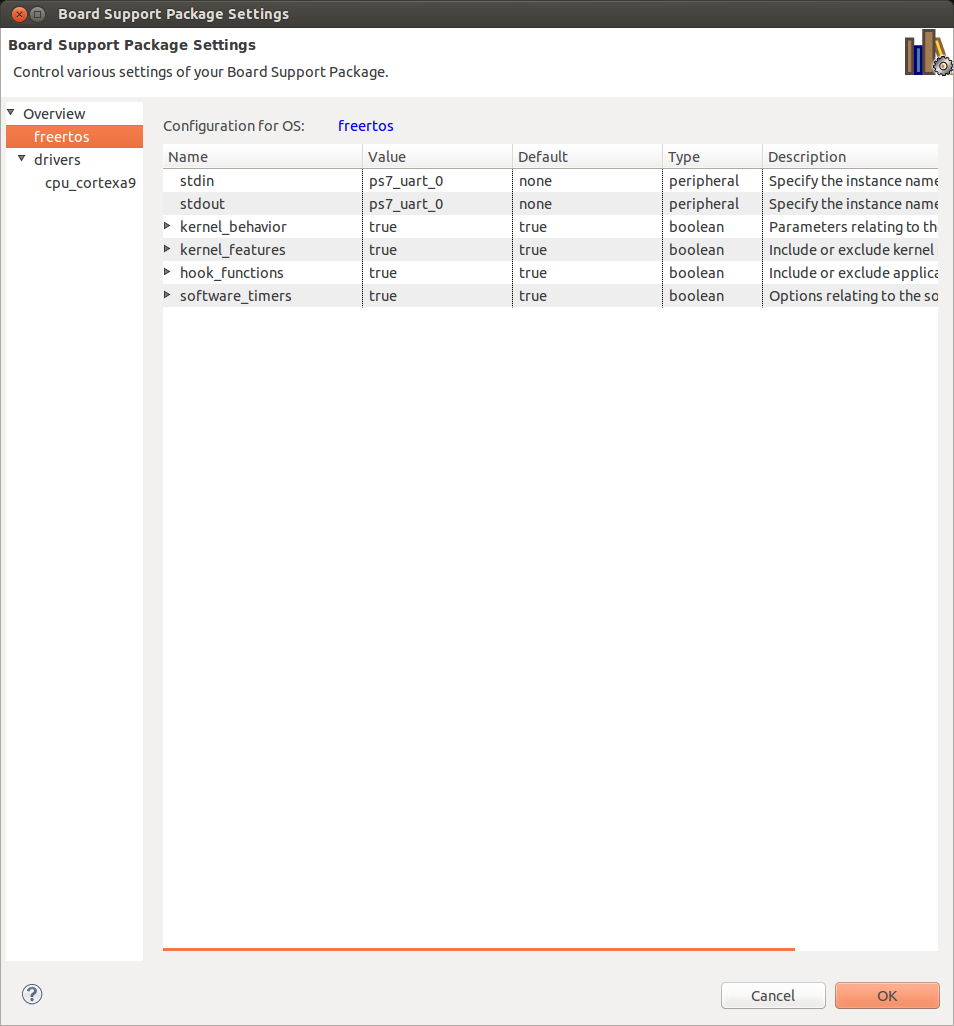
- Create FreeRTOS BSP project. In SDK select File -> New -> Project -> 'Board Support Package'. Name it 'freertos_bsp_amp'. Select 'ZedBoard-AMP-HW' as Hardware Platform, CPU 'ps7_cortexa9_1'. Board Support Package OS 'freertos'. Then Finish.
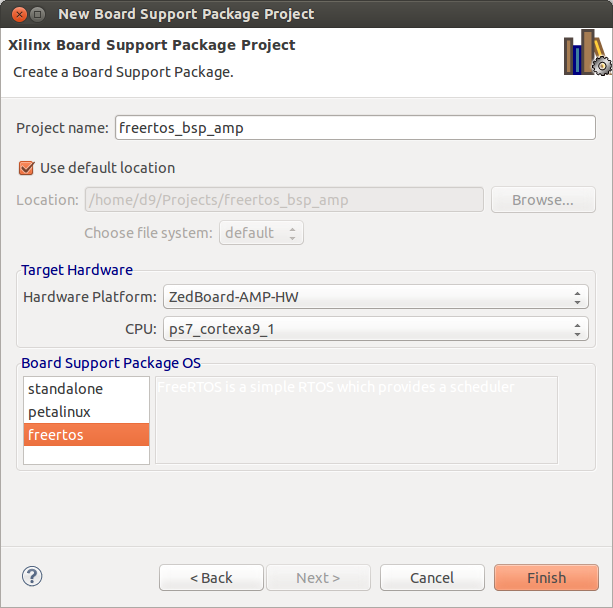
XSDK will automatically open 'Board Support Package Settings' page now for FreeRTOS project. Then:
- 'Overview' -> 'freertos' -> Set 'ps7_uart_0' for both stdin and stdout.
- 'drivers' -> 'cpu_cortexa9' -> Set 'extra_compiler_flags' to '-g -DUSE_AMP=1'.
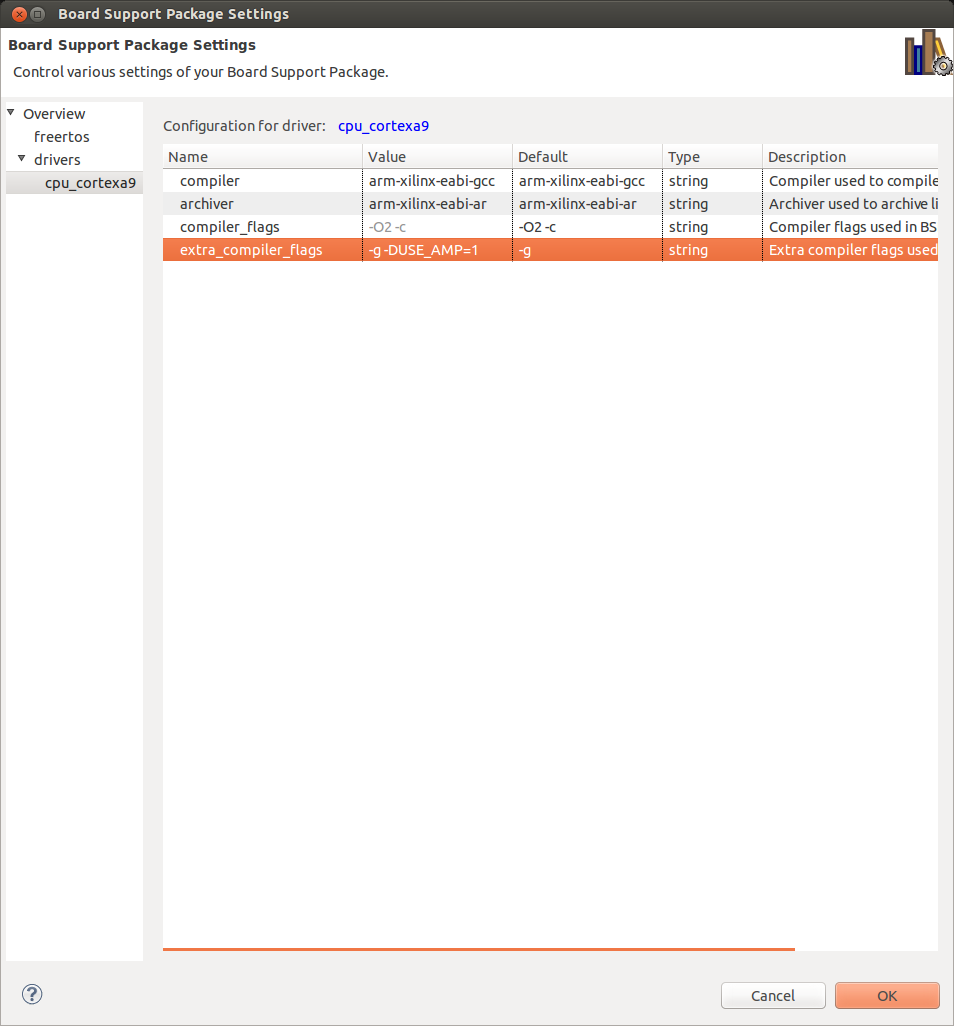
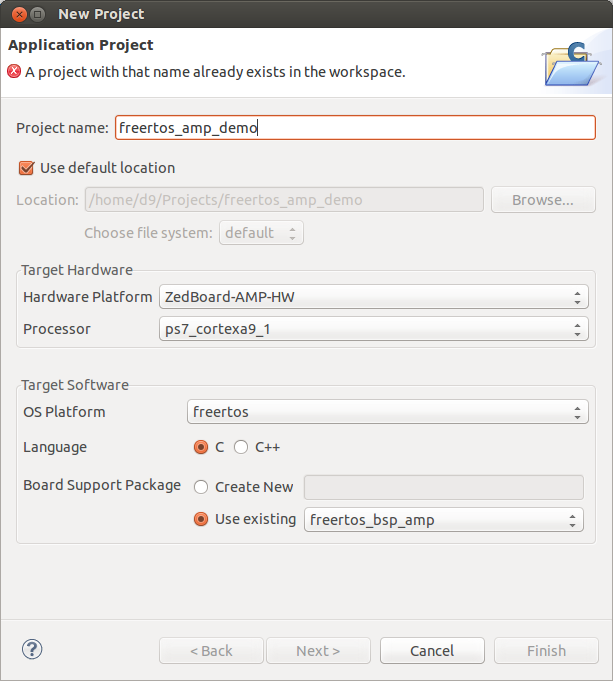
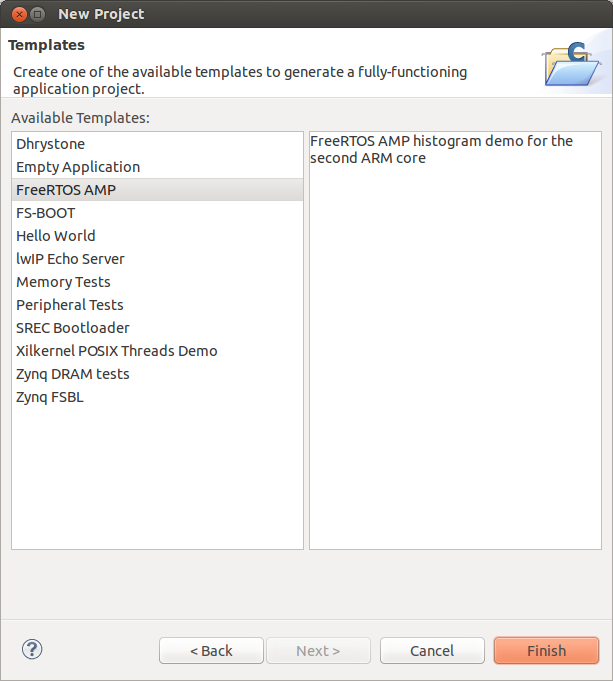
This flag will enable AMP specific features in the FreeRTOS firmware. Hit Ok. And build this project too if it not built automatically. - Create FreeRTOS test applications project. In SDK select File -> New -> Project -> 'Application Project'. Name it 'freertos_amp_demo'. Select 'ZedBoard-AMP-HW' as Hardware Platform, Processor 'ps7_cortexa9_1', OS Platfrom 'freertos', for Board Support Package select 'Use existing' -> then our 'freertos_bsp_amp' project. Click 'Next' and select 'FreeRTOS AMP' template. Click 'Finish'. And build it.
- We are done with XSDK for now. Close it.
- Now we have to create PetaLinux 'project'. And I will name it 'AMP-Demo'.
cd ~/Projects
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi-
source /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2013.4/settings64.sh
source /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/settings.sh
petalinux-create -t project -n AMP-DemoINFO: Create project: AMP-Demo
INFO: New project successfully created in /home/d9/Projects/AMP-Demo - Next step is to adjust our PetaLinux configuration to match our unique 'Hardware Platform' we created using Vivado - 'ZedBoard-AMP'. But we have to do it using BSP we created for our 'Hardware Platform' - 'petalinux_bsp_amp'. So, in a ~/Projects directory:
cd petalinux_bsp_amp/
petalinux-config --get-hw-description -p ../AMP-Demo/INFO: Checking component...
INFO: Getting hardware description...
INFO: Using MSS file /home/d9/Projects/petalinux_bsp_amp/system.mss and XML file /home/d9/Projects/petalinux_bsp_amp/../ZedBoard-AMP-HW/system.xml
INFO: Copy autoconfig for PetaLinux project: /home/d9/Projects/AMP-Demo
INFO: Merging platform settings into kernel configuration
Auto-config file successfully updated for PetaLinux project: /home/d9/Projects/AMP-Demo
[INFO ] generate /home/d9/Projects/AMP-Demo/subsystems/linux/hw-description/system.dts - Verify, that we got the right configuration. In particular, amount of DDR memory - it should be 512M or 0x20000000. Below 'subsystems/linux/hw-description/xparameters.h' file generated in my case:
/* * (C) Copyright 2007-2008 Michal Simek * * Michal SIMEK <monstr@monstr.eu> * * CAUTION: This file is automatically generated by libgen. * Version: Xilinx EDK 2013.4 EDK_2013.4.20131205 * Generate by U-BOOT v4.00.c * Project description at http://www.monstr.eu/uboot/ */ #define XILINX_BOARD_NAME "AMP-Demo" /* ARM is ps7_cortexa9_0 */ #define XPAR_CPU_CORTEXA9_CORE_CLOCK_FREQ_HZ 666666687 /* Interrupt controller is ps7_scugic_0 */ #define XILINX_PS7_INTC_BASEADDR 0xf8f00100 /* System Timer Clock Frequency */ #define XILINX_PS7_CLOCK_FREQ 333333343 /* Uart console is ps7_uart_1 */ #define XILINX_PS7_UART #define XILINX_PS7_UART_BASEADDR 0xe0001000 #define XILINX_PS7_UART_CLOCK_HZ 50000000 /* IIC doesn't exist */ /* GPIO doesn't exist */ /* SDIO controller is ps7_sd_0 */ #define XILINX_PS7_SDIO_BASEADDR 0xe0100000 /* Main Memory is ps7_ddr_0 */ #define XILINX_RAM_START 0x00000000 #define XILINX_RAM_SIZE 0x20000000 /* Flash Memory is ps7_qspi_0 */ #define XILINX_PS7_QSPI_FLASH_BASEADDR 0xE000D000 #define XILINX_SPI_FLASH_MAX_FREQ 50000000 #define XILINX_SPI_FLASH_CS 0 /* Sysace doesn't exist */ /* Ethernet controller is ps7_ethernet_0 */ #define XILINX_PS7_GEM_BASEADDR 0xe000b000
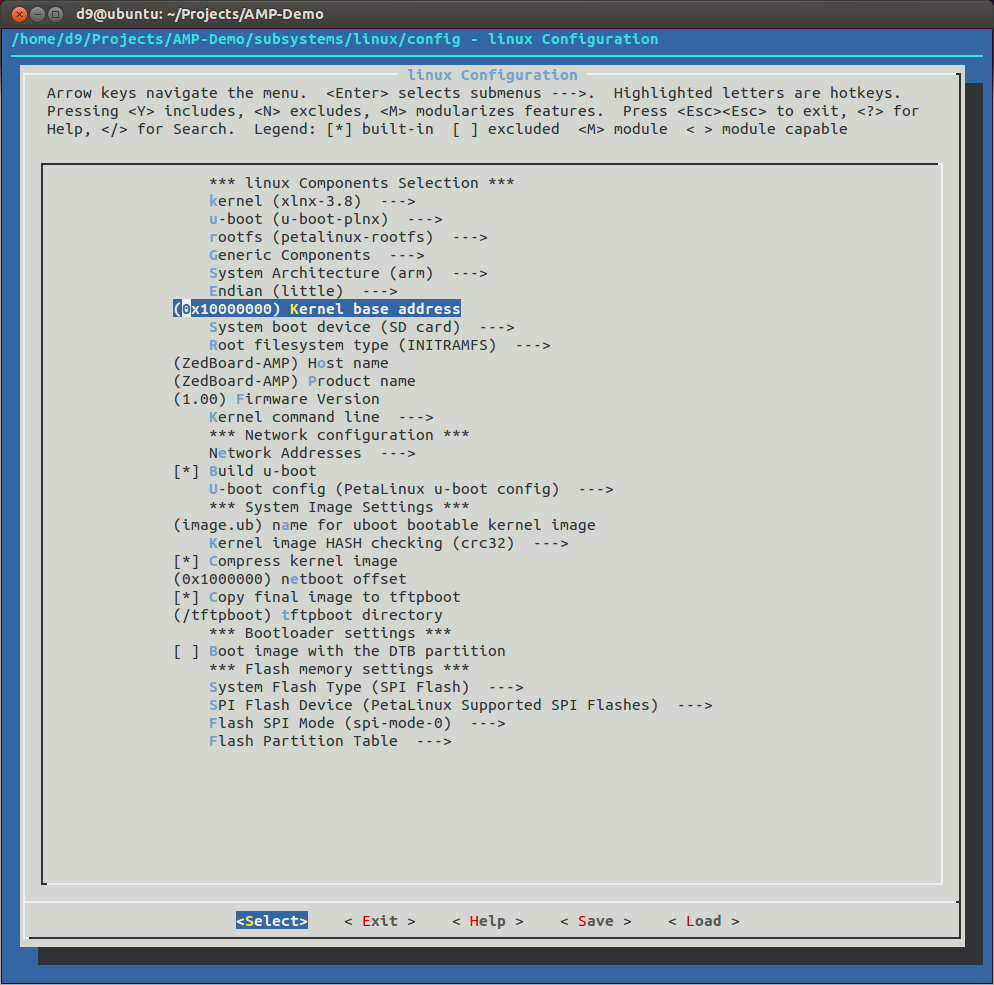
- Next step is to configure our PetaLinux project. AMP system share memory between Linux Kernel and FreeRTOS, so PetaLinux project must be configured to segment the memory and lets split it 256M/256M since our ZedBoard have 512M total of DDR3 memory. I will also change boot media type to SD Card, Host and Product names. So, run petalinux-config and make next this changes:
cd ~/Projects/AMP-Demo/
petalinux-config - Time to configure Linux Kernel for AMP. In a project directory:
petalinux-config -c kernel
In a main page:
- Make sure that 'Enable loadable module support' is selected.
- In 'Kernel Features' -> make sure that 'High Memory Support' is enabled.
- In 'Kernel Features' -> change 'Memory split' to '2G/2G'.
- In 'Device Drivers' -> 'Generic Driver Options' -> make sure 'Userspace firmware loading support' is enabled.
- In 'Device Drivers' -> 'Remoteproc drivers(EXPERIMENTAL)' -> change 'ZYNQ remoteproc' to
(module) and disble Microblaze support. - In 'Device Drivers' -> 'Rpmsg drivers(EXPERIMENTAL)' -> set all three modules to
('An rpmsg server sample', 'rpmsg OMX driver' and 'An FreeRTOS statistic')
Save changes and quit from menuconfig.
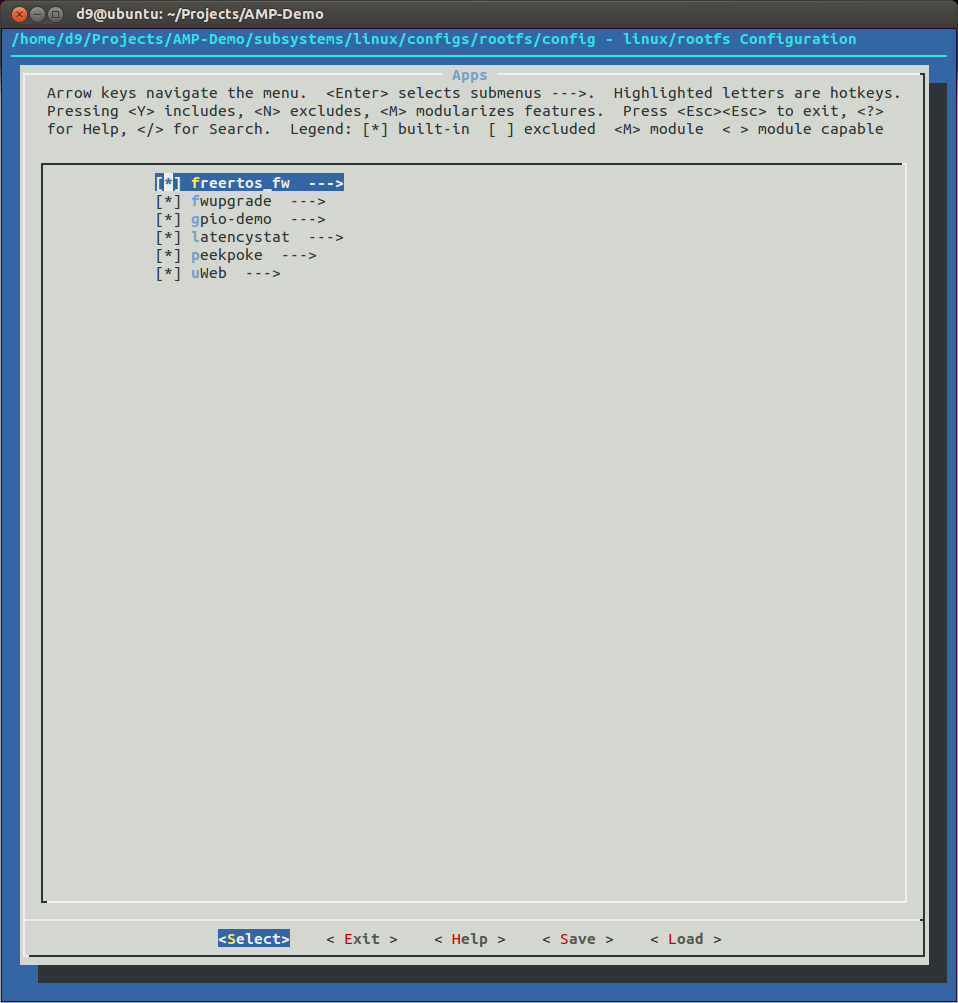
- Configure PetaLinux project ROOTFS. All we need to change now is to in 'Apps-->' menu add/enable 'latencystat' app.
petalinux-config -c rootfs
- Next very important step is to update 'Device Tree Source'(DTS). We need it to do because 'remoteproc' driver instantianated and configured by its node in a device tree.
DTS file we need to modify located in a our petalinux project 'AMP-Demo/subsystems/linux/hw-description/system.dts'. We have to add 'remoteproc' node to 'ps7_axi_interconnect_0' device. Below a portion of my system.dts file. More details regarding 'remoteproc' you can find in a Xilinx UG978 v2013.10:ps7_axi_interconnect_0: amba@0 { #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <1>; compatible = "xlnx,ps7-axi-interconnect-1.00.a", "simple-bus"; ranges ; test: remoteproc-test@0 { compatible = "xlnx,zynq_remoteproc"; reg = < 0x0 0x10000000 >; interrupt-parent = <&ps7_scugic_0>; interrupts = < 0 37 4 0 38 4>; firmware = "freertos"; ipino = <6>; vring0 = <2>; vring1 = <3>; } ; ps7_spi_0: ps7-spi@e0006000 { clock-names = "ref_clk", "aper_clk"; clocks = <&clkc 25>, <&clkc 34>; compatible = "xlnx,ps7-spi-1.00.a"; interrupt-parent = <&ps7_scugic_0>; interrupts = <0 26 4>; num-chip-select = <3>; reg = <0xe0006000 0x1000>; bus-num = <0>; speed-hz = <1000000>; //1000kHz xlnx,has-ss0 = <0x1>; xlnx,has-ss1 = <0x1>; xlnx,has-ss2 = <0x1>; xlnx,spi-clk-freq-hz = <0xF4240>; device@0{ compatible="linux,spidev"; reg =<0>; //CS0 spi-max-frequency= <1000000>; }; device@1{ compatible="linux,spidev"; reg =<1>; //CS1 spi-max-frequency= <1000000>; }; } ; ps7_spi_1: ps7-spi@e0007000 { clock-names = "ref_clk", "aper_clk"; clocks = <&clkc 26>, <&clkc 35>; compatible = "xlnx,ps7-spi-1.00.a"; interrupt-parent = <&ps7_scugic_0>; interrupts = <0 49 4>; num-chip-select = <2>; reg = <0xe0007000 0x1000>; bus-num = <1>; speed-hz = <1000000>; //1000kHz xlnx,has-ss0 = <0x1>; xlnx,has-ss1 = <0x1>; xlnx,spi-clk-freq-hz = <0xF4240>; device@0{ compatible="linux,spidev"; reg =<0>; //CS0 spi-max-frequency= <1000000>; }; device@1{ compatible="linux,spidev"; reg =<1>; //CS1 spi-max-frequency= <1000000>; }; } ; ps7_ethernet_0: ps7-ethernet@e000b000 { #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <0>; clock-names = "ref_clk", "aper_clk"; clocks = <&clkc 13>, <&clkc 30>; compatible = "xlnx,ps7-ethernet-1.00.a"; interrupt-parent = <&ps7_scugic_0>; interrupts = <0 22 4>; local-mac-address = [ 00 0a 35 00 18 e0 ]; phy-handle = <&phy0>; phy-mode = "rgmii-id"; reg = <0xe000b000 0x1000>; xlnx,enet-reset = ""; xlnx,eth-mode = <0x1>; xlnx,has-mdio = <0x1>; xlnx,ptp-enet-clock = <111111115>; mdio { #address-cells = <1>; #size-cells = <0>; phy0: phy@0 { compatible = "marvell,88e1116r"; device_type = "ethernet-phy"; reg = <0>; } ; } ; } ; - Now, with PetaLinux configured, we can add our FreeRTOS demo app we created and compiled using XSDK into PetaLinux rootfs image. In order to do it we can create PetaLinux app using template.
cd ~/Projects/AMP-Demo/
petalinux-create -t apps --template install -n freertos_fwINFO: Create apps: freertos_fw
INFO: New apps successfully created in /home/d9/Projects/AMP-Demo/components/apps/freertos_fw - Copy our FreeRTOS compiled app into PetaLinux apps directory:
cd ~/Projects/AMP-Demo/components/apps/freertos_fw/
cp ../../../../freertos_amp_demo/Debug/freertos_amp_demo.elf data/freertos - Modify 'install' section of Makefile in the app folder:
ifndef PETALINUX $(error "Error: PETALINUX environment variable not set. Change to the root of your PetaLinux install, and source the settings.sh file") endif include $(PETALINUX)/components/apps/apps.common.mk all: build install build: clean: .PHONY: install image install: $(TARGETINST) -d data/freertos /lib/firmware/freertos - Configure PetaLinux 'rootfs' to include this new 'freertos_fw' in 'Apps-->' menu:
cd ~/Projects/AMP-Demo/
petalinux-config -c rootfs - Build PetaLinux project, create BOOT.BIN image using our 'FSBL-AMP' and 'ZedBoard-AMP' bitstream file. Create/update prebuilt configuration.
cd ~/Projects/AMP-Demo/
petalinux-build
petalinux-package --boot --fsbl ../FSBL-AMP/Debug/FSBL-AMP.elf --fpga ../ZedBoard-AMP-HW/system_wrapper.bit --uboot --force -o images/linux/BOOT.BIN
petalinux-package --prebuilt --fpga ../ZedBoard-AMP-HW/system_wrapper.bit --force - Copy BOOT.BIN and image.ub to sd card, set ZedBoard MIO3, MIO4 and MIO5 to 'SD Boot' configuration and turn ZedBoard on.
- Login as 'root'/'root' and verify our kernel version and build timestamp.
root@ZedBoard-AMP:~# uname -a
Linux ZedBoard-AMP 3.8.11 #2 SMP PREEMPT Wed Feb 26 15:39:37 EST 2014 armv7l GNU/Linux
root@ZedBoard-AMP:~# - Because we included remoteproc as a module and it not loaded yet - Linux must be using both CPU's in a conventional SMP way. Lets verify it:
more /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 0 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 1332.01 Features : swp half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x3 CPU part : 0xc09 CPU revision : 0 processor : 1 model name : ARMv7 Processor rev 0 (v7l) BogoMIPS : 1332.01 Features : swp half thumb fastmult vfp edsp neon vfpv3 tls CPU implementer : 0x41 CPU architecture: 7 CPU variant : 0x3 CPU part : 0xc09 CPU revision : 0 Hardware : Xilinx Zynq Platform Revision : 0000 Serial : 0000000000000000
- Now, lets load remoteproc driver:
modprobe zynq_remoteproc
CPU1: shutdown remoteproc0: 0.remoteproc-test is available remoteproc0: Note: remoteproc is still under development and considered experimental. remoteproc0: THE BINARY FORMAT IS NOT YET FINALIZED, and backward compatibility isn't yet guaranteed.
modprobe rpmsg_freertos_statistic
remoteproc0: powering up 0.remoteproc-test remoteproc0: Booting fw image freertos, size 2130820 remoteproc0: remote processor 0.remoteproc-test is now up virtio_rpmsg_bus virtio0: rpmsg host is online virtio_rpmsg_bus virtio0: creating channel rpmsg-timer-statistic addr 0x50 rpmsg_freertos_statistic rpmsg0: new channel: 0x400 -> 0x50!
So, second Processor unloaded from Linux and is setup to execute the FreeRTOS firmware.
- Now, we can run 'latencystat' FreeRTOS demo app.
latencystat -b
Linux FreeRTOS AMP Demo. 0: Command 0 ACKed 1: Command 1 ACKed Waiting for samples... 2: Command 2 ACKed 3: Command 3 ACKed 4: Command 4 ACKed ----------------------------------------------------------- Histogram Buckvirtio_rpmsg_bus virtio0: msg received with no recepient et Values: Bucket 341 ns (38 ticks) had 14813 frequency Bucket 431 ns (48 ticks) had 1 frequency Bucket 521 ns (58 ticks) had 1 frequency Bucket 593 ns (66 ticks) had 1 frequency Bucket 692 ns (77 ticks) had 1 frequency ----------------------------------------------------------- Histogram Data: min: 341 ns (38 ticks) avg: 341 ns (38 ticks) max: 692 ns (77 ticks) out of range: 0 total samples: 14817 ----------------------------------------------------------- root@ZedBoard-AMP:~#
- Access the TraceBuffer - a section of shared memory which is only written to by the FreeRTOS application. This
TraceBuffer used as a logging console to transfer information to Linux and 'latencystat' app uses it. So, lets check it out:more /sys/kernel/debug/remoteproc/remoteproc0/trace0
Congratulation! We got Linux-FreeRTOS AMP configuration running on our ZedBoard.
mkdir Projects
cd Projects
source /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2013.4/settings64.sh
xsdk
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-xilinx-linux-gnueabi-
source /opt/Xilinx/Vivado/2013.4/settings64.sh
source /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/settings.sh
xsdk
I have followed all of these instructions exactly, but I'm afraid there is something wrong with my environment. When I get to the step petalinux-build, I get an error that says "no architecture is defined" and the build fails. Does anyone know what the source of this problem is?
I should also note that I am using CentOS 6.5 64 bit and not Ubuntu
Can you post whole log?
Is this what you wanted to see?
[root@localhost AMP-Demo]# petalinux-build -c all
WARNING: Your PetaLinux project was last modified by PetaLinux SDK version "2013.04",
WARNING: however, you are using PetaLinux SDK version "2013.10".
Please input "y" to continue. Otherwise it will exit![n]y
INFO: Checking component...
INFO: Generating make files and build linux
INFO: Generating make files for the subcomponents of linux
INFO: Building linux
[ERROR] /opt/petalinux-v2013.10-final/etc/build/common.mk:17: *** "No architecture is defined!". Stop.
[ERROR] make[1]: *** [sub_pre-build_component_/none/apps/multi/freertos_fw] Error 2
ERROR: Failed to build linux
Oh boy.
Remove Petalinux 2013.4, and recreate AMP-Demo project using 2013.10. They changed a lot of thing between this two versions of Petalinux.
I did create the AMP-DEMO with 2013.10. I did everything with 2013.10. I installed 2013.4 after the fact just as a test to see if I could get that one working. The problem is with 2013.10
Heh, can you post original then?
In general, good place to start digging into the problem is petalinux build log. It's located in petalinux project 'build' directory.
I followed your instructions on Ubuntu 13.10 64 bit and it works. I'm not sure what the deal was with CentOS 6.5 64 bit.
I would have preferred to use CentOS since that is where all of my other development is done. If a solution to that problem is ever found, please post it.
Nevermind that problem. This stemmed from the fact that I didn't use the right board from Vivado. I chose the ZC702 instead of the avnet version 7Z020. Once I recreated a project using the right board I had no problem making it work. Beautiful post. One thing I had to do that I noticed wasn't in here though is that I had to make a symbolic link from make to gmake so that the Vivado tools would build the projects.
Thanks for this guide, works perfectly.
Hi, thanks for the guide, it worked in Software, all the steps worked fine with Petalinux and Xilinx SDK.
But, when i had tried to Boot with BOOT.BIN and image.ub, I got U-boot working, but the Linux Kernel Didn't boot.
Could you suggest what should be the solution for that ?..
What kernel version did you try?
I am using petalinux 2013.10 as you have mentioned, so, i think the version should be same as yours.
Following is my log, when i was booting the ZedBoard.
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Terminal ready
.... MEOT !
BOTP bradcat 1
BOP brodcast 2
BOOTPbroadcast
BOT broacast 4
BOOTP broadcast 5
Retry count exceeded
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
SF: Detected S25FL256S_64K with page size 64 KiB, total 32 MiB
SF: 11010048 bytes @ 0x520000 Read: OK
Wrong Image Format for bootm command
ERROR: can't get kernel image!
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Still, U-boot is working, so i had tried to do with "run bootcmd" command, but it didn't work
here is the log.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
U-Boot-PetaLinux> run bootcmd
SF: Detected S25FL256S_64K with page size 64 KiB, total 32 MiB
SF: 11010048 bytes @ 0x520000 Read: OK
Wrong Image Format for bootm command
ERROR: can't get kernel image!
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I have followed all the steps what should be the problem ?
Well, your U-boot settings got screwed somehow. Try to google it. Maybe try to reset them to defaults.
Yes, so In Boot mode, It was QSPI for the default petalinux u-boot configuration.
by changing it with petalinux-config, the design worked
Thanks for the guide.